The oral microbiome is not a random collection of microscopic organisms. Instead, it is a community of microbes that functions to protect and maintain optimal oral health. This diverse system of microbes exists in harmony, working to prevent common problems such as cavities, gum disease, and bad breath. When in a healthy state, the oral microbiome serves as a natural defense mechanism, regulating harmful bacteria and promoting a balanced environment within the mouth.
However, an imbalance in this system can lead to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria, increasing the risk of dental problems and uncomfortable symptoms. In this article, we’ll explore how beneficial microbes in the oral microbiome work to keep your mouth balanced and what you can do to support this microscopic team in defending against cavities, gum disease, and bad breath. Understanding this process will empower you to make simple choices that promote a healthier, fresher mouth and better overall wellness.
The Role of the Oral Microbiome in Cavity Prevention
The oral microbiome plays a pivotal role in preventing tooth decay by minimizing the presence of harmful bacteria and helping to create a balanced and healthy environment in your mouth. Here’s how it works:

Overview of Cavity Formation
Cavity formation, or dental caries, is a gradual process that results from the interaction between bacteria, sugars, and tooth enamel. It begins when bacteria in the mouth break down sugars from food, producing acids that erode the enamel, the tooth’s protective outer layer.
- Plaque Formation: A sticky biofilm of bacteria forms on teeth, especially after consuming sugary or starchy foods.
- Acid Production: Bacteria produce acids as they digest sugars, leading to enamel demineralization.
- Demineralization: Initial loss of minerals creates white spots on teeth, indicating early decay.
- Cavity Development: Continued acid exposure weakens enamel, forming cavities that require dental intervention.
- Progression: If untreated, decay can reach deeper layers of the tooth, causing pain and potential infection.
Understanding this process highlights the importance of good oral hygiene and dietary choices in preventing cavities.
Protective Mechanisms
The oral microbiome is crucial in preventing tooth decay through various protective mechanisms. Beneficial bacteria form biofilms on tooth surfaces, creating a barrier against harmful pathogens. This dynamic ecosystem maintains a balance that is essential for oral health.
- Biofilm Formation: Beneficial bacteria create a protective layer on teeth, limiting access for harmful bacteria.
- Nutrient Competition: They compete with pathogenic bacteria for resources, reducing their growth.
- Antimicrobial Production: Some beneficial bacteria produce substances that inhibit harmful microbes.
- Remineralization: They aid in remineralizing enamel, which helps strengthen teeth against decay.
- pH Regulation: The microbiome helps neutralize acids that contribute to tooth erosion.
These mechanisms collectively help maintain oral health and reduce the risk of cavities.
Impact of Diet and Hygiene
Diet and oral hygiene are critical factors influencing dental health and the prevention of tooth decay. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can strengthen teeth and gums, while poor dietary choices can lead to significant oral health issues.
- Sugary Foods: High sugar intake fuels harmful bacteria, leading to tooth decay and cavities.
- Acidic Foods: Foods like citrus fruits and sodas can erode enamel, making teeth more vulnerable.
- Calcium-Rich Foods: Foods such as leafy greens help fortify teeth against decay.
- Hydration: Drinking water aids in rinsing away food particles and bacteria, preventing plaque buildup.
- Mindful Eating: Limiting snacking reduces acid exposure and promotes better oral health.
Maintaining good dietary habits and proper oral hygiene are essential for a healthy smile.
How the Oral Microbiome Fights Gum Disease
The oral microbiome is critical in protecting against gum disease by supporting healthy gums and reducing harmful bacteria. Here’s how it contributes to gum health:
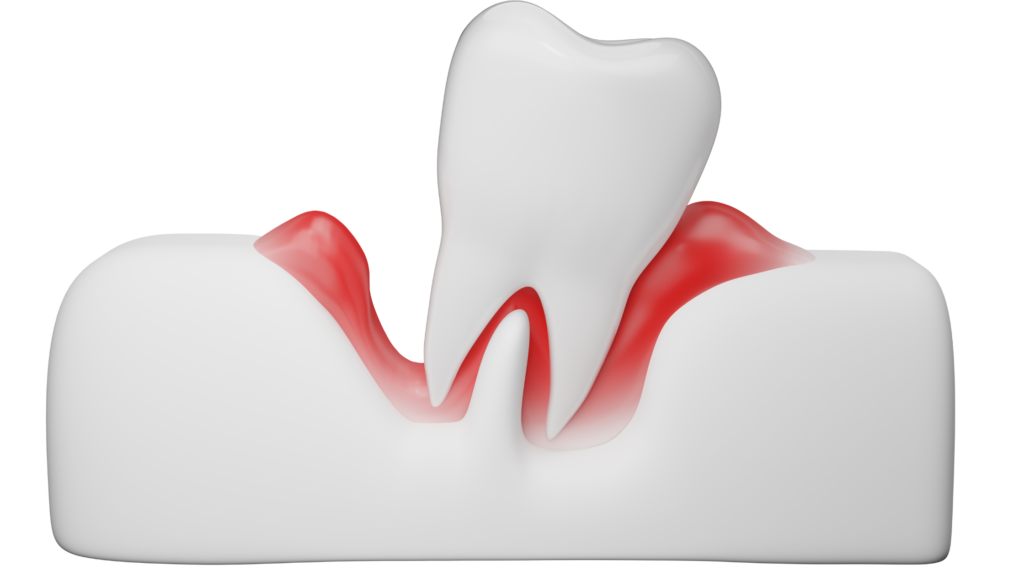
Understanding Gum Disease
- Definition: Gum disease, which includes gingivitis and periodontitis, is an inflammatory condition affecting the gums. Gingivitis is milder and is characterized by red, swollen gums, while periodontitis is more severe and can lead to bone loss and tooth loss.
- Primary Causes: Gum disease typically develops due to bacterial plaque buildup along the gumline. When left untreated, this plaque triggers an inflammatory response that can damage gum tissue and lead to disease progression.
Role of Beneficial Bacteria
- Anti-Inflammatory Compounds: Certain beneficial bacteria in the oral microbiome produce compounds that reduce inflammation, helping to protect the gums from irritation and swelling.
- Balanced Microbiome: A balanced microbiome prevents the overgrowth of harmful bacteria contributing to gum disease. Beneficial bacteria compete for resources, limiting the ability of disease-causing bacteria to thrive and cause gum inflammation.
Influence of Lifestyle Choices
- Diet: A diet rich in fiber and nutrients helps support beneficial bacteria, strengthening their role in defending against gum disease.
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the microbiome, weakening its protective effects and increasing the risk of gum inflammation.
- Hygiene: Consistent brushing and flossing remove plaque, supporting the beneficial bacteria that help prevent gum disease.
By fostering a balanced oral microbiome through diet, stress management, and regular hygiene, you can significantly reduce your risk of gum disease and maintain healthier gums.
Preventing Bad Breath with a Balanced Oral Microbiome

A balanced oral microbiome is essential for maintaining fresh breath, as it helps control the growth of odor-causing bacteria. Here’s how it works:
Causes of Bad Breath
- Sulfur-Producing Bacteria: Bad breath is often caused by bacteria that produce sulfur compounds, which have an unpleasant odor.
- Food Particles: When food particles remain in the mouth, they fuel bacteria, leading to increased bacterial activity and unpleasant odors.
Protective Role of Beneficial Bacteria
- Outcompeting Odor-Causing Bacteria: Beneficial bacteria help maintain a balanced microbiome by outcompeting bacteria that produce sulfur, which naturally helps keep breath fresher.
- Breaking Down Food Particles: The microbiome also aids in breaking down food particles more efficiently, reducing the number of odor-causing residues in the mouth.
Importance of Hydration and Saliva
- Saliva’s Role: Saliva is essential for supporting a healthy microbiome, as it provides nutrients for beneficial bacteria and helps wash away food particles.
- Preventing Dry Mouth: Staying hydrated promotes saliva production, preventing dry mouth—a common cause of bad breath due to reduced microbial balance.
By supporting a balanced oral microbiome through hydration and good hygiene, you can minimize bad breath and enjoy fresher, healthier breath.
Tips to Support an Oral Microbiome that Protects Against Common Issues
Supporting a healthy oral microbiome is essential for preventing common dental issues such as cavities and gum disease. Here are key tips to nurture this complex ecosystem:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush twice daily and floss regularly to remove plaque and food particles that disrupt the microbial balance.
- Use Probiotic Dental Products: Incorporate probiotic toothpaste and mouthwash to introduce beneficial bacteria into your mouth.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, and fermented products like yogurt, which promote microbial diversity.
- Reduce Sugar Intake: Limit sugary and acidic foods that feed harmful bacteria and contribute to enamel erosion.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to support saliva production, which helps cleanse the mouth and neutralize acids.
- Avoid Tobacco and Alcohol: These substances can harm the microbiome and increase the risk of oral diseases.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Schedule routine visits to monitor oral health and receive personalized recommendations.
By implementing these strategies, you can foster a balanced oral microbiome that protects against common dental issues.
Conclusion
The oral microbiome serves as a natural defense system, helping to prevent cavities, gum disease, and bad breath by maintaining a balanced environment in the mouth. By making daily choices like eating a high-fiber, low-sugar diet, staying hydrated, and practicing consistent oral hygiene, you can support a healthy microbiome that benefits both your oral and overall health. Continue following this series to gain deeper insights into optimizing your oral health and harnessing the power of a balanced microbiome for lasting wellness.